When battling heart disease, you may be familiar with balloon angioplasties and stenting. For carotid artery disease, a condition in which the arteries in the neck that deliver blood to the brain become blocked or narrowed, this procedure can be used instead of surgery. Carotid angioplasty and stenting are now equally effective and safe as surgical carotid endarterectomy in treating blockages in the arteries of the neck.
Carotid Angioplasty and Stenting: What Happens During the Procedure?
Carotid angioplasty and stenting may be used to treat a significant blockage in a carotid artery that does not necessitate surgery. Interventional cardiologists, vascular surgeons, and radiologists are among the doctors who are trained in catheter-based therapy and execute the procedure.
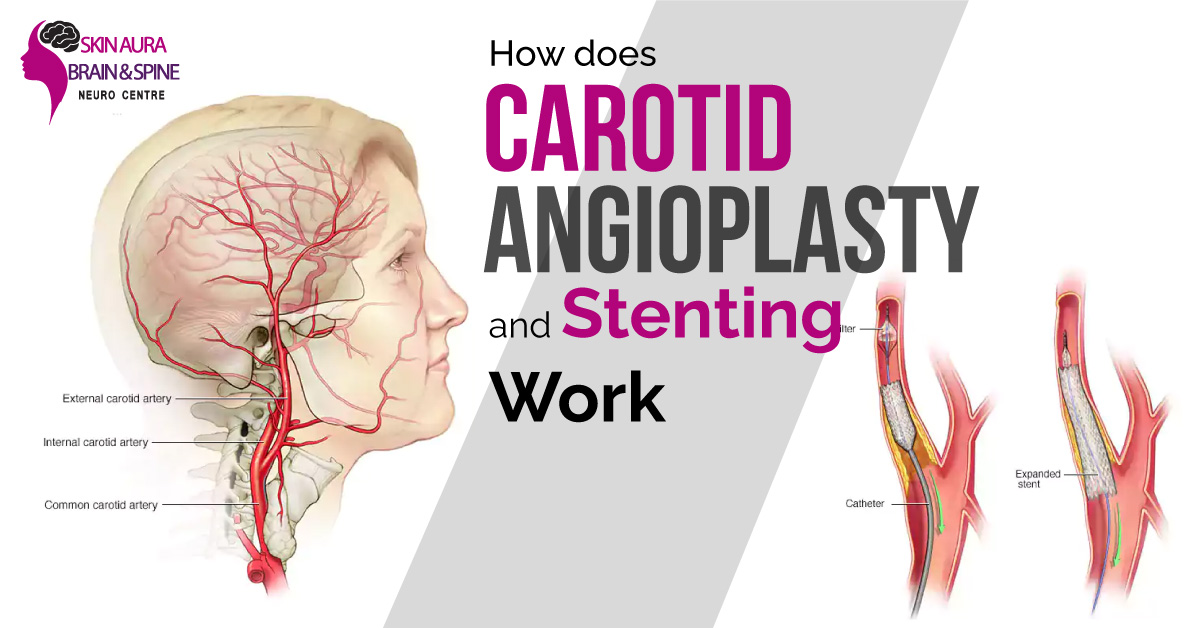
Plaque, a fatty substance that builds up in the arteries and narrows or blocks them, is the hallmark of carotid artery disease. To restore blood flow to the brain, the procedure of carotid angioplasty and stenting involves inserting a thin tube called a catheter into the damaged carotid artery and then propping it open with an expandable mesh tube called a stent.
Before the Procedure, What Can I Expect?
On the day of the procedure, members of your care team at Skin Aura Brain and Spine Neuro Center will provide you with detailed instructions, including information on what to eat, drink, and cease taking before the surgery.
Catheterization laboratories, or “cath labs,” conduct carotid angioplasty and stenting. Your catheter insertion site will be numbed with local anesthesia, and you will be given relaxation medicines to help you relax during the process.
In the course of the procedure, what can you expect?
Angioplasty is a procedure in which a thin tube (the catheter) is run through an artery and up to the carotid arteries in the neck, where the blockage is located, generally near the groin. Live x-ray imaging is used to guide this procedure. Using a small inflated balloon, the artery is widened, and the plaque is pushed to the outside of the wall. Plaque and other debris may fall out of the balloon during the opening process.
During the surgery, a distal protection device (a tiny umbrella-like device) captures this debris, dramatically reducing the risk of stroke. The physician may then insert a stent to prevent the artery from narrowing again.
Preparation time will increase the procedure’s length by around two hours. The interventional cardiologist may converse with you to keep an eye on blood flow to the brain.
After the procedure, what should you expect?
After a carotid angioplasty and stenting surgery, patients typically remain in the hospital for two days. This time in the hospital gives the patient a chance to recuperate and for the doctor to keep an eye on their progress.
Patients are given instructions on what activities they should avoid and how long when they leave the hospital. Even if it’s just for 24 hours, you may be instructed to refrain from moving heavy objects or engaging in strenuous physical activity.
You’ll be alerted by your medical team if you see any of the warning indicators listed below:
Confusion, trouble speaking or understanding, or numbness or weakness on one side of the body are signs of a stroke. Your leg puncture wound becomes redder, dripping more pus, or hurting when no pressure is applied—swelling where the catheter was placed.
Angioplasty and stenting may be necessary because of what?
If you suffer from carotid artery stenosis, this treatment may be necessary. The carotid arteries, either one or both, are narrowed in this condition. Due to the accumulation of plaque, carotid stenosis is often produced. Atherosclerosis is the medical term for this. Several factors can cause carotid stenosis. Smoking, high cholesterol, high blood pressure, obesity, diabetes, and aging are all factors that contribute to heart disease.
Carotid artery stenosis might cause symptoms in certain persons. Examples are vision issues or a loss of neurologic function in a particular body area. The restricted carotid artery also has the potential to develop a blood clot. A clot in the bloodstream that makes its way to the brain may cut off oxygen-rich blood flow to the area. A stroke is a medical term for this type of event. It can cause brain damage and even death in some people.
The risk of stroke can be reduced if you have minor carotid artery stenosis by taking drugs prescribed by your doctor.
Carotid Stenting in Gurgaon
The best Doctor may recommend a procedure to open the artery if your blockage is more severe. An earlier stroke or mini-stroke means your doctor is more likely to prescribe surgery.
One alternative is carotid angioplasty and stenting. A third option is a procedure known as carotid endarterectomy. Plaque and any damaged arterial tissue are removed during this procedure.
Although your recovery from the actual surgery is often fast, it is merely the beginning of the process of protecting your heart and brain from the dangers of a stroke, heart attack, or other cardiovascular condition. Slow, halt, or reverse the underlying disease process that causes blockages in your carotid arteries and affects all of your body’s arteries by making lifestyle changes and taking prescribed drugs exactly as prescribed.