DEEP BRAIN STIMULATION SURGERY
Definition
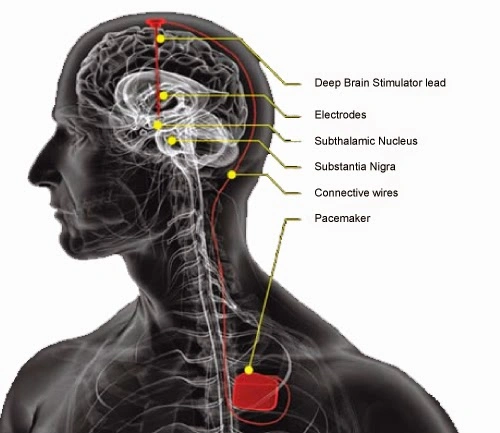
Deep Brain Stimulation(DBS) is a surgery that involves implanting of electrodes in specific targets of brain. Electrical impulses are produced by these electrodes to regulate any abnormal impulses in the brain. The amount of stimulation that the brain receives in this procedure is controlled by a medical device called a neurostimulator also referred to as a ‘brain pacemaker’, placed in the upper chest, under the patient's skin. A wire travels under the skin to connect this device to the electrodes.
What is its use?
Deep Brain Stimulation is used to treat various neurological conditions responsible for a number of movements controlled by the nervous system. It is done only when a patient is unable to get control of the symptoms with simple medication.
Movement disorders that can be treated with deep brain stimulation treatment:
- Chronic pain
- Dystonia
- Essential tremor
- Epilepsy
- Obsessive compulsive disorder
- Parkinson's disease
- Tourette syndrome
Risks in Surgical Procedure
Surgery is always done by a medical specialist preferably by a Neurosurgeon and is generally a safe procedure to help improve bodily function. However, rare risks involved are as under.
Surgery Complications in DBS:
- Bleeding in the brain
- Stroke
- Infection
- Breathing problems
- Nausea
- Heart problems
- Seizures
Possible Side Effects Of Stimulation
After successful completion of the Deep Brain Stimulation surgery, the neurostimulator is turned on after a few days. It may take some time to find the best setting that suits a patient's body in particular, which may result in some temporary side effects:
- Muscle tightness of the face or arm
- Numbness or tingling sensations
- Balance problems
- Speech problems
- Unwanted mood changes, such as mania and depression
- Lightheadedness
These side effects will however improve with the adjustments made to the device.
All you need to know about the surgery:
You need to undergo some medical tests before taking the surgery, to make sure that deep brain stimulation is a safe option for you. An MRI, before the surgery, is also needed to map the areas of your brain to implant the electrodes.
How the surgery works?
Deep brain stimulation surgery is divided into two portions:
- Brain surgery
- Chest wall surgery
Brain surgery: In this portion, at first, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is done to identify the area in your brain to place the electrodes, making the head still using stereotactic head frame. Local Anesthesia is given to numb your scalp before the frame fixation and undergo final CT brain. After fusion of CT images with MRI Brain , Targets are planned on computers. Patient is shifted to OT and under mild sedation 2 holes(Burr holes) are done in Skull Bone according to targets. After that, the surgeon implants a thin wire lead with a number of contacts (electrodes) at the targeted area of the brain. And, a wire runs under your skin to the pulse generator (neurostimulator) implanted near the collarbone.
To help your neurologist and neuroanaesthetist check the simulations in the brain, you'll be kept awake in most of the cases during the procedure as your responses will help in placing the electrodes in the right place, minimizing the side effects.
Chest wall surgery: This is the second portion of the surgery, which is done under General anesthesia. It mainly consists of implanting the pulse generator under the skin of your chest. Wires from the electrodes placed in the brain are guided down to the battery-operated pulse generator.
The pulse generator consists of batteries and is programmed to send electrical pulses to the brain. It comes with a special remote, using which you can turn it on or off.
It is important for you to know that deep brain stimulation is not always successful for everyone. There are a number of factors involved in the success of this surgery. Therefore, it is important for you to talk with a specialised doctor , Neurosurgeon before surgery about what type of improvement you can expect for your condition.



